Occupational Illnesses Copy
OCCUPATIONAL INJURIES & ILLNESSES
An occupational illness is an event or exposure that occurs in the workplace that causes or contributes to a condition or worsens a preexisting condition.
An occupational injury is the result of a specific on-the-job accident. The date and cause of such an accident can be determined with precision. An occupational disease is a condition that occurs over time. It can cause chronic symptoms and ailments that prevent you from doing your job.
- Back pain
- Occupational COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease)
- Occupational Asthma.
- Occupational Hearing Loss
- Eyesight Deterioration
- Occupational Skin Disease
- Occupational Dermatitis.
- Occupational Musculoskeletal Disorders. Poor Manual Handling Techniques including incorrect Display Screen Equipment set up
- Hearing Loss due to load equipment or work processes.
Occupational skin diseases are ranked among the top five occupational diseases in many countries. Occupational skin diseases and conditions are generally caused by chemicals and having wet hands for long periods while at work. Eczema is by far the most common, but urticaria, sunburn and skin cancer are also of concern.

OCCUPATIONAL HEALTH
Under the Occupational Health and Safety Act, Occupational illness is defined as a condition that results from exposure in a workplace to a physical, chemical or biological agent to the extent that the normal physiological mechanisms are affected and the health of the worker is impaired.
HOW CAN CHEMICALS BE HAZARDOUS TO HEALTH?
Chemicals can cause many different types of harm, ranging from mild skin irritation to cancer. The effects of hazardous chemicals may be seen:
- Immediately after contact (e.g. chemical burn) or many years after the exposure (e.g. lung cancer following exposure to asbestos).
- Following a single short exposure (e.g. infrequent use of a chemical)
- or longer-term exposures (e.g. daily use of a chemical in the workplace).
It is important to minimise exposure to chemicals at all times. In order for a chemical to be hazardous to a person’s health, it must either be in contact with or enter the body.
CATEGORIES OF HAZARDOUS CHEMICALS
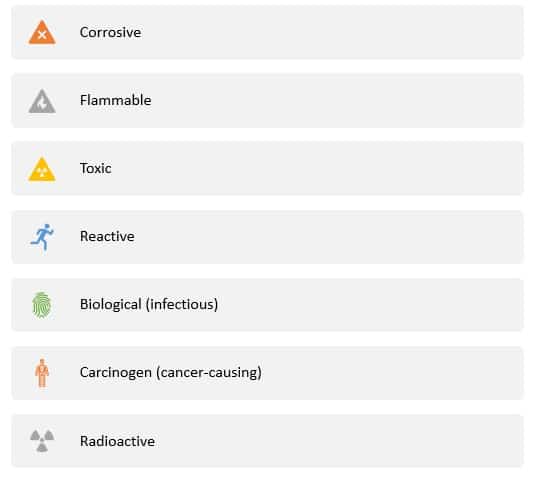
TOXICITY

Chronic Toxicity – the development of adverse effects as a result of long term exposure to a contaminant or other stressor.
Chronic exposure is continuous or repeated contact with a toxic substance over a long period of time (months or years). If a chemical is used every day on the job, the exposure would be chronic. Over time, some chemicals, such as PCBs ( Poly Chlorine Biphenyl) and lead, can build up in the body. Health effects that have been associated with exposure to PCBs include acne-like skin conditions in adults and neurobehavioral and immunological changes in children. PCBs are known to cause cancer in animals.
Polychlorinated biphenyls(PCBs) are aromatic, synthetic chemicals which do not occur naturally in the environment. They consist of the biphenyl structure with two linked benzene rings in which some or all of the hydrogen atoms have been substituted by chlorine atoms.
OCCUPATIONAL DISEASES ASSOCIATED WITH CHEMICAL USE
- Occupational Asthma –
- Occupational Dermatitis
- Lung Disease
- Breathing Difficulties
- Carcinogens
- Occupational Dermatitis – A skin Infection, red raw, cracked skin.
- Effects on Brain & Nervous System – exposure to pesticides, mercury, lead, solvents, carbon monoxide gas.
- Eyes, Nose & Throat irritation
- Liver damage – exposure to vinyl chloride.
- Bladder damage – exposure to some azo dyes (bladder cancer).
- Effects on blood & bone marrow – exposure to benzene in petrol fumes (anaemia and leukaemia).

IMPORTANT: Always use the PPE provided as intended.